程序流程结构
C/C++ 支持最基本的三种程序运行结构:顺序结构 、选择结构 、循环结构
-
顺序结构:程序按顺序执行,不发生跳转
-
选择结构:依据条件是否满足,由选择的执行相应功能
-
循环结构:依据条件是否满足,循环多次执行某段代码
顺序结构
示例
xusing namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 0;
cout << "第一次输出:" << a + 1 << endl;
cout << "第二次输出:" << a + 2 << endl;
cout << "第三次输出:" << a + 3 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

选择结构
作用:执行满足条件的语句
if 语句的三种形式
-
单行格式 if 语句
-
多行格式 if 语句
-
多条件的 if 语句
单行格式 if 语句
if (条件) {条件满足执行的语句}
示例
xxxxxxxxxx
if (a != 0) {cout << "a 不等于 0" << endl;}
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//选择结构 单行 if 语句
//用户输入分数,如果分数大于 600 ,视为考上一本大学,并再屏幕上输出
//1、用户输入分数
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入一个分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
//2、打印用户输入的分数
cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;
//3、判断分数是否大于 600 ,如果大于,那么输出
if (score > 600) {
cout << "恭喜您考上了一本大学" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

多行格式 if 语句
if (条件) {条件满足执行的语句}else {条件不满足执行的语句}
示例
xxxxxxxxxx
if (a != 0) {cout << "a 不等于 0" << endl;}else {cout << "a 等于 0" << ednl;}
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//选择结构 多行 if 语句
//输入考试分数,如果分数大于 600,时为考上一本大学,并在屏幕上输出
//如果没考上一本大学,打印未考上一本大学
int score = 0;
//1、输入考试分数
cout << "请输入您的考试分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
//2、提示用户输入分数
cout << "您的考试分数为:" << score << endl;
//3、判断 如果大于 600,打印考上一本,否则打印未考上一本
if (score > 600) {
cout << "您考上了一本" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "您未考上一本" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

多条件的 if 语句
if (条件1) {条件1满足执行的语句} else if (条件2) {条件2满足执行的语句}… else{所有条件均不满足执行的语句}
示例
xxxxxxxxxx
if (a >=0 && a < 10) {
cout << "您的成绩不及格" << endl;
}else if(a >=10 && a < 20) {
cout << "您的成绩及格" << endl;
}else if (a >= 20 && a < 30) {
cout << "您的成绩优秀" << endl;
}else if (a = 30) {
cout << "您的成绩为满分" << endl;
}else {
cout << "您的成绩不合法" << endl;
}
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//选择结构 多条件 if 语句
//输入一个考试分数,如果大于 600 分,视为考上一本大学,并在屏幕输出
//大于 500 分,视为考上二本大学。并在屏幕输出
//大于 400 分,视为考上三本大学,并在屏幕输出
//小于等于 400 分,视为考上本科,并在屏幕输出
//1、用户输入分数
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入您的分数" << endl;
cin >> score;
//2、提示用户输入的分数
cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;
//3、判断
if (score > 600) {
cout << "您考上了一本大学" << endl;
}else if (score > 500 && score <= 600) {
cout << "您考上了二本大学" << endl;
}else if (score > 400 && score <= 500) {
cout << "您考上了三本大学" << endl;
}else if (score <= 400 && score >= 0) {
cout << "您考上了本科" << endl;
}else {
cout << "您的成绩不合法" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

嵌套 if 语句
在 if 语句中,可以嵌套使用 if 语句,达到更精确的条件判断
需求
-
提示用户输入一个高考考试分数,根据分数做如下判断
-
分数如果大于
600分视为考上一本,大于500分考上二本,大于400分考上三本,其余视为未考 -
在一本分数中,如果大于
700分,考入北大,大于650分,考入清华,大于600考入人大
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//提示用户输入一个高考考试分数,根据分数做出判断
// 分数如果大于 600 分视为考上一本,大于 500 分考上二本,大于 400 分考上三本,其余视为未参与考试
//在一本分数中,如果大于 700 分,考入北大,大于 650 分,考入清华。大于 600 分考入人大
//用户输入分数
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入考试的分数" << endl;
cin >> score;
//显示输入的分数
cout << "您的分数为:" << score << endl;
//判断
if (score > 600) {
if (score > 700)
{
cout << "您考上了北大" << endl;
}
else if (score > 650 && score <= 700) {
cout << "您考上了清华" << endl;
}
else if (score > 600 && score <= 650) {
cout << "您考上了人大" << endl;
}
}
else if (score > 500 && score <= 600) {
cout << "您考上了二本" << endl;
}
else if (score > 400 && score <= 500) {
cout << "您考上了三本" << endl;
}
else if (score >= 0 && score <= 400) {
cout << "您未参加考试" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "您的成绩不合法" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

案例 – 三只小猪称体重
有三支小猪 A、B、C,分别输入三只小猪的体重,并且判断哪只小猪最重
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//初始化三只小猪的体重
int Pig1 = 0;
int Pig2 = 0;
int Pig3 = 0;
//用户输入三只小猪的重量
cout << "请输入第一只小猪的重量" << endl;
cin >> Pig1;
cout << "请输入第二只小猪的重量" << endl;
cin >> Pig2;
cout << "请输入第三只小猪的重量" << endl;
cin >> Pig3;
cout << '\n' << "三只小猪的重量为:" << '\n' <<
"第一只小猪" << '\t' << Pig1 << '\n' <<
"第二只小猪" << '\t' << Pig2 << '\n' <<
"第三只小猪" << '\t' << Pig3 << '\n' << endl;
if (Pig1 > Pig2) {
if (Pig1 > Pig3) {
cout << "第一支小猪最重" << endl;
}
else if (Pig1 < Pig3) {
cout << "第三只小猪最重" << endl;
}
}
else if (Pig1 < Pig2) {
if (Pig2 > Pig3)
{
cout << "第二只小猪最重" << endl;
}
else if (Pig2 < Pig3) {
cout << "第三只小猪最重" << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

三目运算符
作用:通过三目运算符实现简单的判断
语法:
xxxxxxxxxx
表达式1 ? 表达式2 : 表达式3
如果表达式1的值为真,执行表达式2,并返回表达式2的结果
如果表达式1的值为假,执行表达式3,并返回表达式3的结果
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 0;
c = (a > b ? a : b);
cout << "c的值为:" << c << '\n' << endl;
//在 C++ 中,三目运算符返回的是变量。所以可以继续赋值
(a > b ? a : b) = 100;
cout << "a的值为:" << a << endl;
cout << "b的值为:" << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

switch 语句
作用:执行多条件分支语句
示例
xxxxxxxxxx
switch (表达式){
case 结果1: 执行语句;break;
case 结果1: 执行语句;break;
···
default:执行语句;break;
}
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//switch
//给电影进行打分
// 10-9 经典
// 8-7 非常好
// 6-5 一般
// 5以下 烂片
int Rating = 0;
//1、提示用户给电影打分
cout << "请给电影打分" << endl;
//2、用户开始进行打分
cin >> Rating;
//3、根据用户输入的分数来提示用户最后的结果
switch (Rating)
{
case 10:
cout << "您认为是经典电影" << endl;
break;
case 9:
cout << "您认为是经典电影" << endl;
break;
case 8:
cout << "您认为该电影非常好" << endl;
break;
case 7:
cout << "您认为该电影非常好" << endl;
break;
case 6:
cout << "您认为该电影一般" << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "您认为该电影一般" << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "您认为该电影是烂片" << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "您认为该电影是烂片" << endl;
break;
case 2:
cout << "您认为该电影是烂片" << endl;
break;
case 1:
cout << "您认为该电影是烂片" << endl;
break;
case 0:
cout << "您认为该电影是烂片" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "您输入的分数不合法" << endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

if 和 switch 区别
switch
-
缺点:判断时,只能是整型或者字符型,不可以是一个区间
-
优点:结构清晰,执行效率高
每一个执行区间中要填写 break 防止出现 case穿透
循环结构
while 循环
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
语法
xxxxxxxxxx
while(循环条件){循环语句}
只要循环条件的结果为真,就一直执行循环语句
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//while循环
//在屏幕中打印 0-9 这10个数字
int num = 0;
while (num <= 9) {
cout << num << endl;
num++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

案例 – 猜数字
系统随机生成一个 1 到 100 之间的数字,玩家进行猜测,如果猜错,提示玩家数字过大或者过小,如果猜对恭喜玩家胜利,并且退出游戏
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
//time系统时间头文件包含
int main() {
//添加随机数种子 利用当前系统事件生成随机数,防止每次随机数都一样
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//1、系统生成随机数
int num = rand() % 100 + 1;
int Input = -1;
cout << "请输入您猜测的数字" << endl;
//2、玩家进行猜测
while (Input != num) {
cin >> Input;
if (Input > num) {
cout << "您输入的数字过大,请重新输入" << endl;
}
else if (Input < num) {
cout << "您输入的数字过小,请重新输入" << endl;
}
}
cout << "您输入的数字正确" << endl;
//3、判断玩家的猜测
//猜对 退出游戏
//猜错 提示猜的结果 过大或者过小 重新返回让玩家猜测
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

do…while 循环语句
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
注意:与 while 的区别在于 do…while 会先执行一次循环语句,在判断循环条件
语法
xxxxxxxxxx
do {循环语句} while(循环条件);
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//do...while语句
//在屏幕中输出 0到9 这10个数字
int num = 0;
do
{
cout << num << endl;
num++;
} while (num < 10);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

案例 – 水仙花数
水仙花数是指一个 3 位数,它的每个位上的数字的 3次幂之和 等于他本身
例如: 1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3 =153
利用 do…while 语句,求除所有3位数中的水仙花数
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、将所有的三位数进行输出(100-999)
int num = 100;
int OnePlace = 0;
int TenPlace = 0;
int HundredPlace = 0;
do
{
OnePlace = num % 10;
TenPlace = (num / 10) % 10;
HundredPlace = num / 100;
//2、找出所有三位数的水仙花数
/*
* 获取个位 数字 % 10 = 数字个位 对数字取模于10 可以获取到个位
*
* 获取十位 (数字 / 10) % 10 = 数字十位
* 因为 C++ 中 int 类型相除会将结果的小数部分舍去,获得的结果再取模则可获得相应的位数
*
* 获取百位 数字 / 100 = 数字百位
*/
if (((OnePlace * OnePlace * OnePlace) + (TenPlace * TenPlace * TenPlace) + (HundredPlace * HundredPlace * HundredPlace)) == num)
{
cout << num << endl;
}
num++;
} while (num < 1000);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

for 循环语句
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
注意:for 循环中的表达式,要用分号进行分隔
语法
xxxxxxxxxx
for(其实表达式;条件表达式;末尾表i大师) {循环语句;}
示例
xxxxxxxxxx
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
cout << i << endl;
}
例如
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main(){
//for 循环
//从数字0 打印到 数字99
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

案例 – 敲桌子
从 1 开始数到是数字 100,如果数字个位含有7,或者数字十位含有7,或者该数字是7的倍数,就打印敲桌子,其余数字直接打印输出
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
int OnePlace = 0;
int TenPlace = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
OnePlace = i % 10;
TenPlace = (i / 10) % 10;
if (i % 7 ==0 || OnePlace == 7 || TenPlace == 7) {
cout << "敲桌子" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << i << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

嵌套循环
再循环体中再嵌套一层循环,解决一些实际问题
使用方式
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i <=10 ; i++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
cout << "* ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

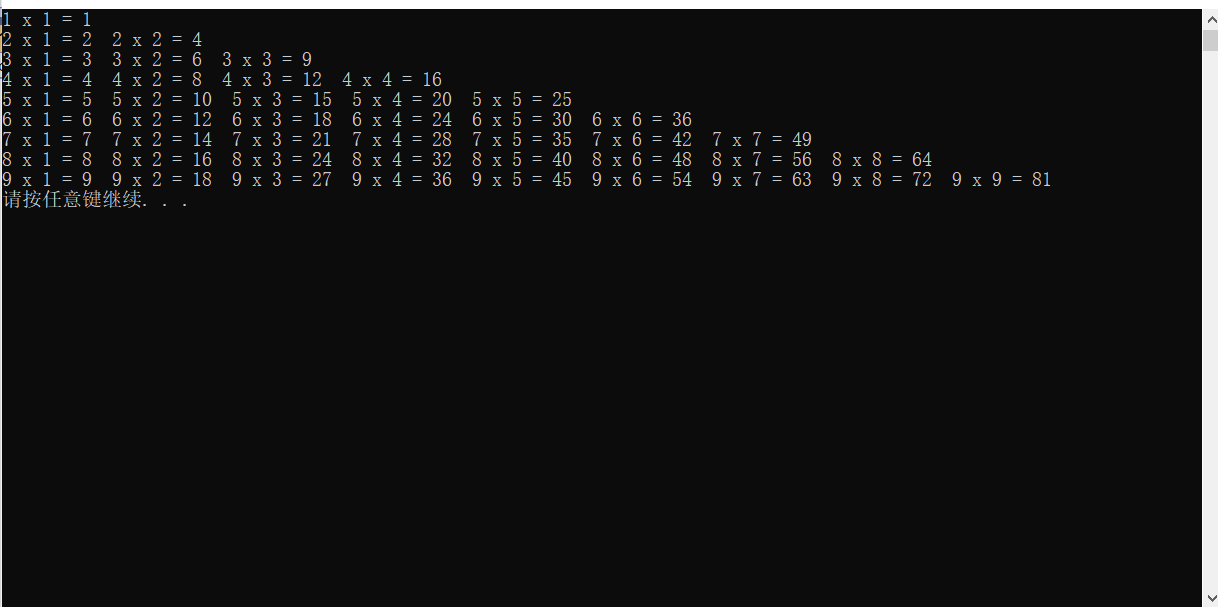
案例 – 乘法口诀表
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) {
if (j <= i)
{
cout << i << " x " << j << " = " << i * j << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行
跳转语句
作用:用于跳出选择结构或者循环结构
使用时机:
-
出现再 switch 条件语句中,作用是终止 case 并跳出 switch
-
出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前的循环语句
-
出现在嵌套循环中,跳出最近的内层循环语句
switch 语句中
x
using namespace std;
int main(){
//1、出现在 switch 语句中
cout << "请选择副本难度" << endl;
cout << "1、简单" << endl;
cout << "2、普通" << endl;
cout << "3、困难" << endl;
cout << "4、史诗" << endl;
int select = -1;
cin >> select;
switch (select)
{
case 1:
cout << "您选择了简单难度" << endl;
break;
case 2:
cout << "您选择了普通难度" << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "您选择了困难难度" << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "您选择了史诗难度" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "您选择了错误的难度" << endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

循环语句
x
using namespace std;
int main(){
//2、出现在循环语句中
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << i << endl;
if (i == 7)
{
break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行
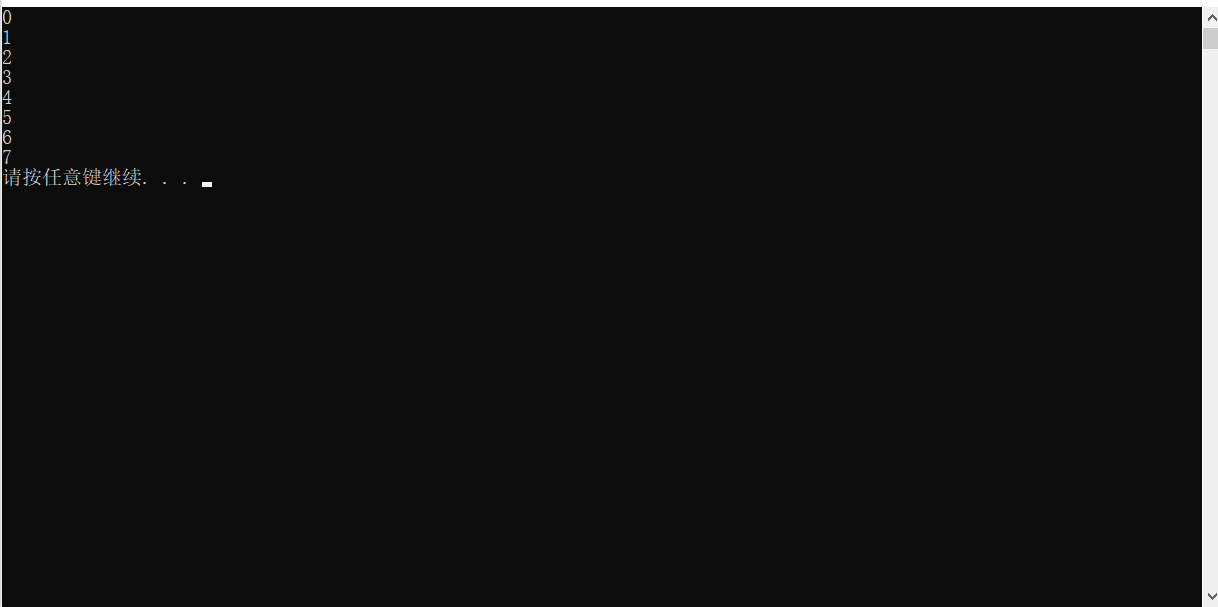

嵌套循环
x
using namespace std;
int main(){
//3、出现在嵌套循环语句中
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= 10; j++) {
cout << "* ";
if (i == 6&& j == 7)
{
break;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

continue 语句
作用:再循环语句中,跳过本次循环中余下尚未执行的语句,继续执行下一次循环
使用方式
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (i> 4 && i < 6)
{
continue;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行

goto 语句
作用:可以无条件跳转语句
注意:在程序中不建议使用 goto 语句,以免造成程序流程混乱
语法
xxxxxxxxxx
goto 标记;
如果标记的名称存在,执行到 goto 语句时,会跳转到标记的位置
使用方式
xxxxxxxxxx
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "1" << endl;
cout << "2" << endl;
cout << "3" << endl;
goto flag;
cout << "4" << endl;
cout << "5" << endl;
cout << "6" << endl;
cout << "7" << endl;
flag:
cout << "8" << endl;
cout << "9" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行
